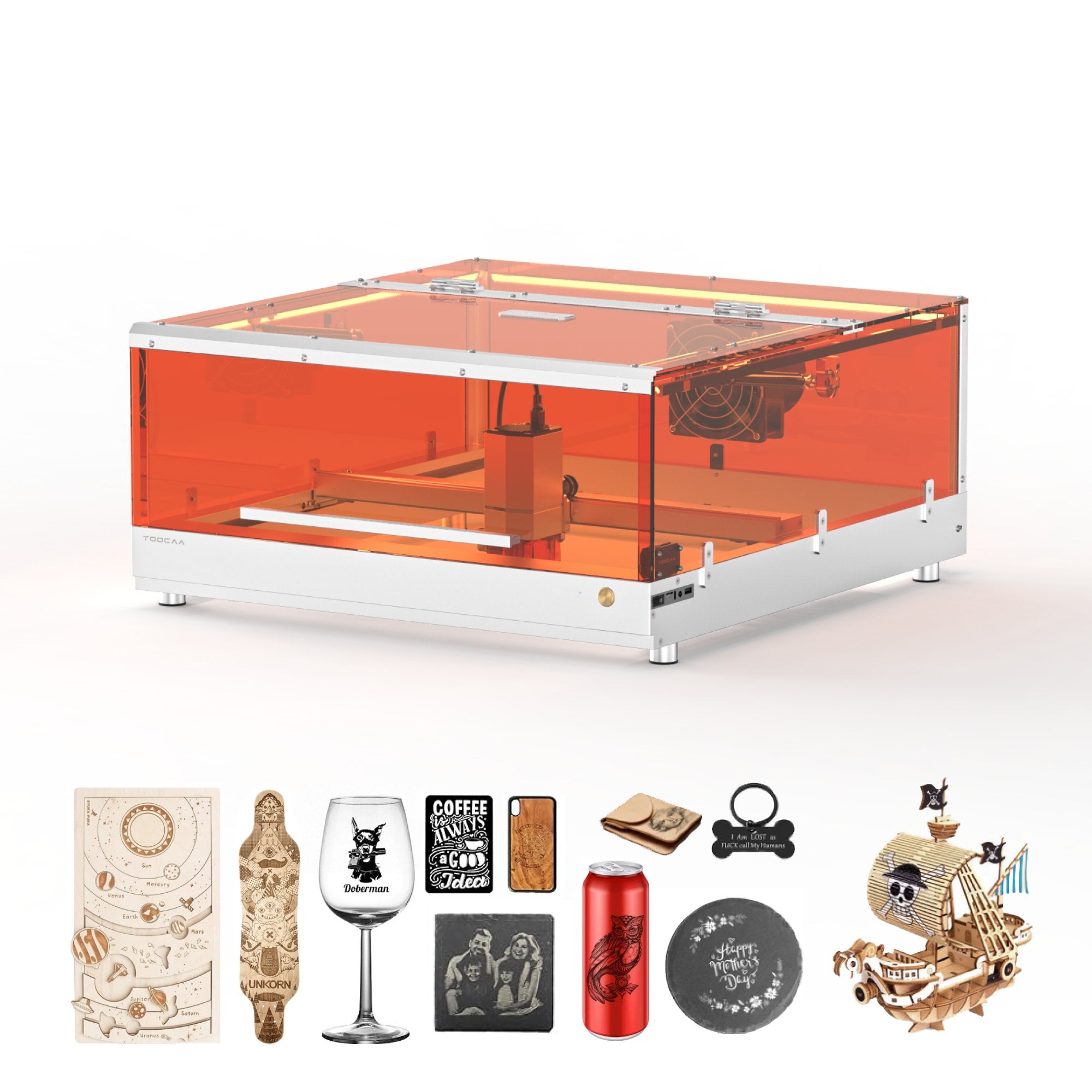
Laser engraving is a cutting-edge technology renowned for its precision and versatility, widely utilized in various industries for marking, personalization, and enhancing materials.
From custom gifts and intricate designs to industrial applications and functional components, laser engraving provides exceptional accuracy and durability.

This advanced process utilizes a focused beam of light to meticulously etch or remove material, creating detailed and permanent marks that are both aesthetically pleasing and highly functional.
Exploring the Mechanics of Laser Engraving
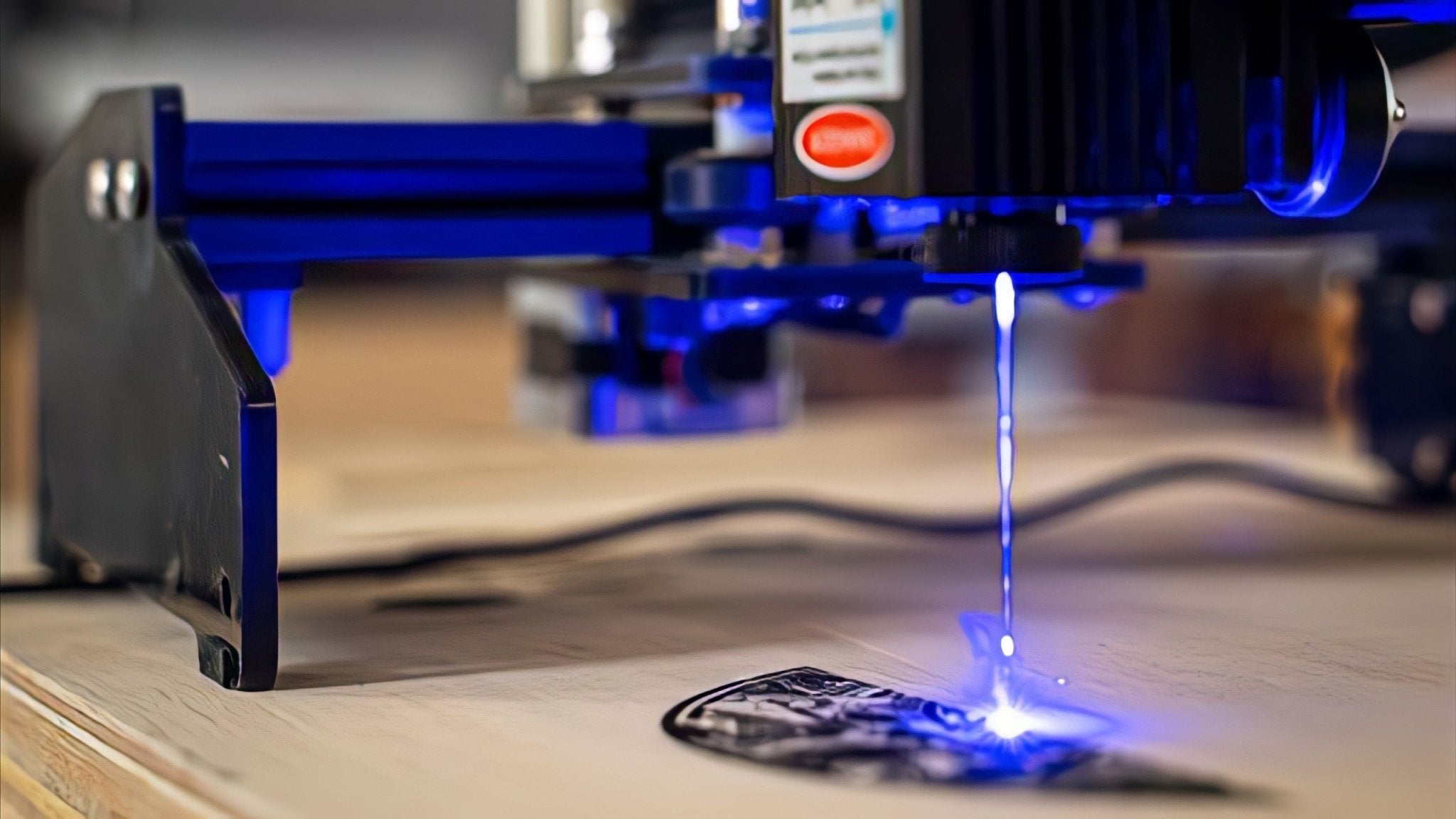
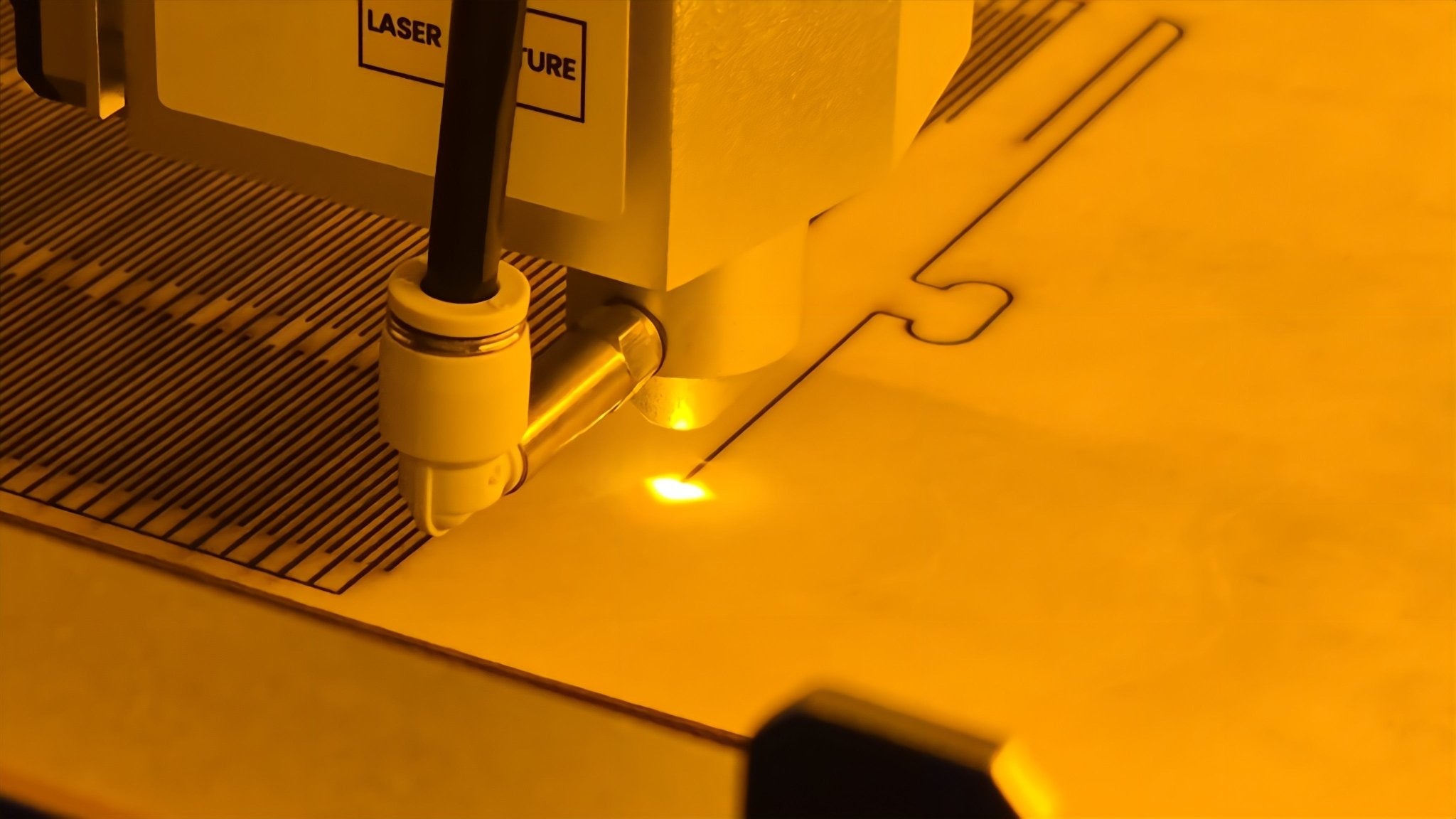
Laser engraving operates on the principle of using a concentrated beam of light to interact with a material’s surface. This interaction removes or vaporizes the material, based on its properties, to produce a detailed engraving.
The process is controlled by sophisticated software that translates digital designs into precise laser movements. This allows for the creation of complex patterns, text, logos, and designs with remarkable accuracy.

Types of Lasers Used for Engraving
1. CO2 Laser
- Wavelength: 10.6 micrometers
- Applications: Ideal for non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, and leather.
- Features: Versatile for carving and engraving a variety of materials, making it a popular choice for many applications.
2. Fiber Laser
- Wavelength: 1.06 micrometers
- Applications: Perfect for metal engraving, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Features: Known for its high efficiency and low maintenance, fiber lasers deliver fine engravings with precision.
3. UV Laser
- Wavelength: 355 nanometers
- Applications: Suitable for delicate materials like plastics, ceramics, and glass.
- Features: Provides precise and clean markings without causing heat damage to the material.
Main Components of a Laser Engraving System
- Laser Light Source
Function: Emits the laser beam used for engraving. The type of laser source depends on the material and precision required.
- Laser Optical System
Function: Includes lenses and mirrors to focus and direct the laser beam onto the material. The quality of the optics affects engraving precision and clarity.
- Control System
Function: Typically a computer that controls the laser's movement and the material's placement. It interprets design files and translates them into precise engraving instructions.
- Workbench
Function: The surface on which materials are placed. Adjustable workbenches can accommodate various sizes and shapes of materials.
The Engraving Process

- Design Preparation
Create a design using graphic design software.
Convert the design into a format compatible with the laser engraver.
- Material Placement
Position the material on the workbench, ensuring it is securely fixed to prevent movement during engraving.
- Parameter Settings
Adjust the laser settings such as power, speed, frequency, and focus according to the material and the desired depth of engraving.
- Engraving
The laser engraver begins the process, moving the laser beam across the material as per the design file.
The beam removes material layer by layer to create the engraving.
- Post-Processing
After engraving, clean the material to remove any debris and residue.
Additional treatments like polishing or coating may be applied to enhance the appearance and durability.
Factors Affecting Laser Engraving Quality
- Material Properties
Different materials react differently to laser engraving. For instance, metals require more effort compared to plastics. The quality depends on material composition and thickness.
- Laser Parameters
Proper settings for power, speed, and frequency are crucial. Incorrect parameters can lead to reduced contrast or excessive material removal.
- Focus and Alignment
Accurate focusing and alignment of the laser beam are vital for clarity. Misalignment can result in distorted or blurry engravings.
- Environmental Conditions
Factors like temperature, humidity, and ventilation can influence the engraving process. Proper ventilation is needed to clear smoke and debris.
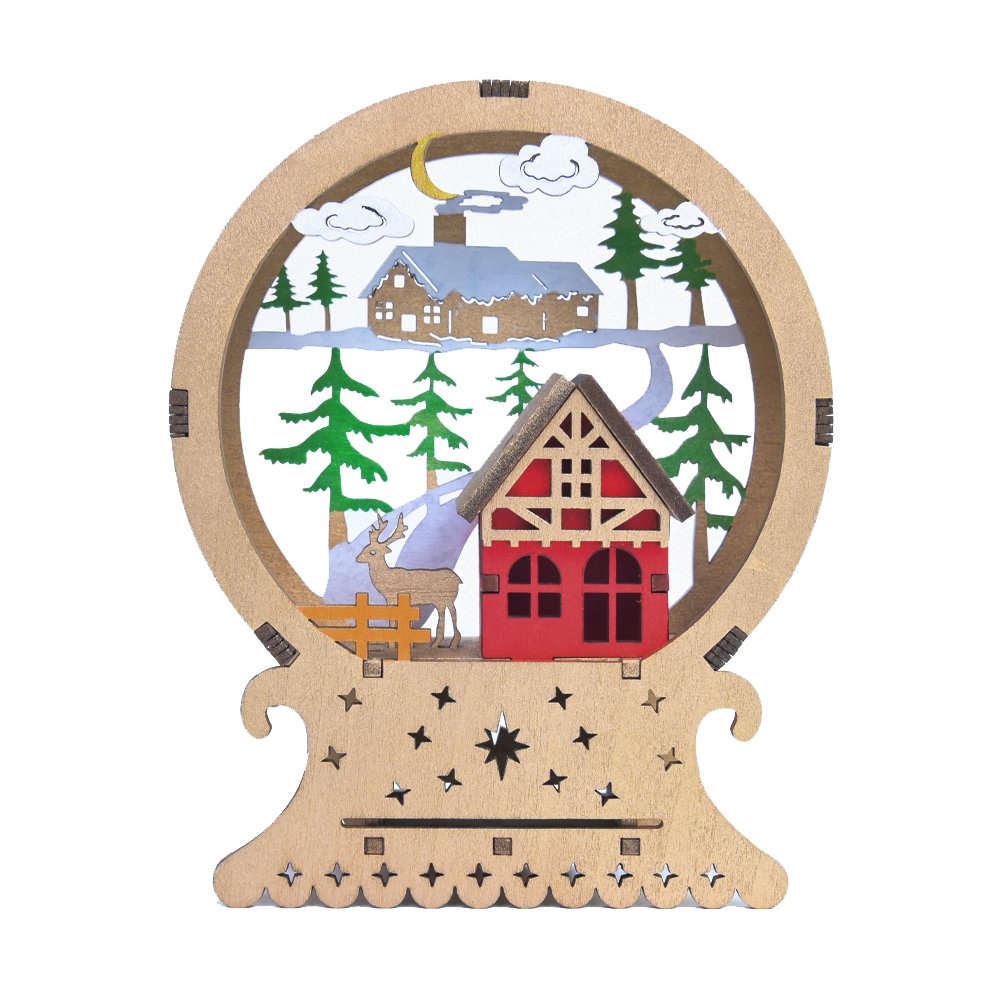
Examples of Laser Engraving Applications
-
Industrial Marking: Used for marking parts with identification numbers, barcodes, and logos in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
-
Jewelry and Personalization: Adds names, dates, or designs to jewelry and gifts, making them unique and memorable.
-
Promotional Materials: Displays logos and messages on items like pens, keychains, and merchandise.
-
Decorative Arts: Artists create detailed patterns and designs on various materials for artistic projects.
Conclusion
Laser engraving is a sophisticated technology offering precision, versatility, and durability. By understanding the types of lasers, the components of the engraving system, and the factors affecting quality, you can appreciate the complexities and possibilities of this process.
Whether for industrial use, commercial purposes, or personal projects, laser engraving remains an invaluable tool for creating detailed and lasting marks on a wide range of materials.

A fiber laser can carve super intricate designs into any metal in just 10 seconds. Have you ever wondered how it is done?
I am very thrilled to recommend this video. With the introduction of Alexander Sellite, let's watch these lasers in slow motion, and learn about fiber lasers and how they function.